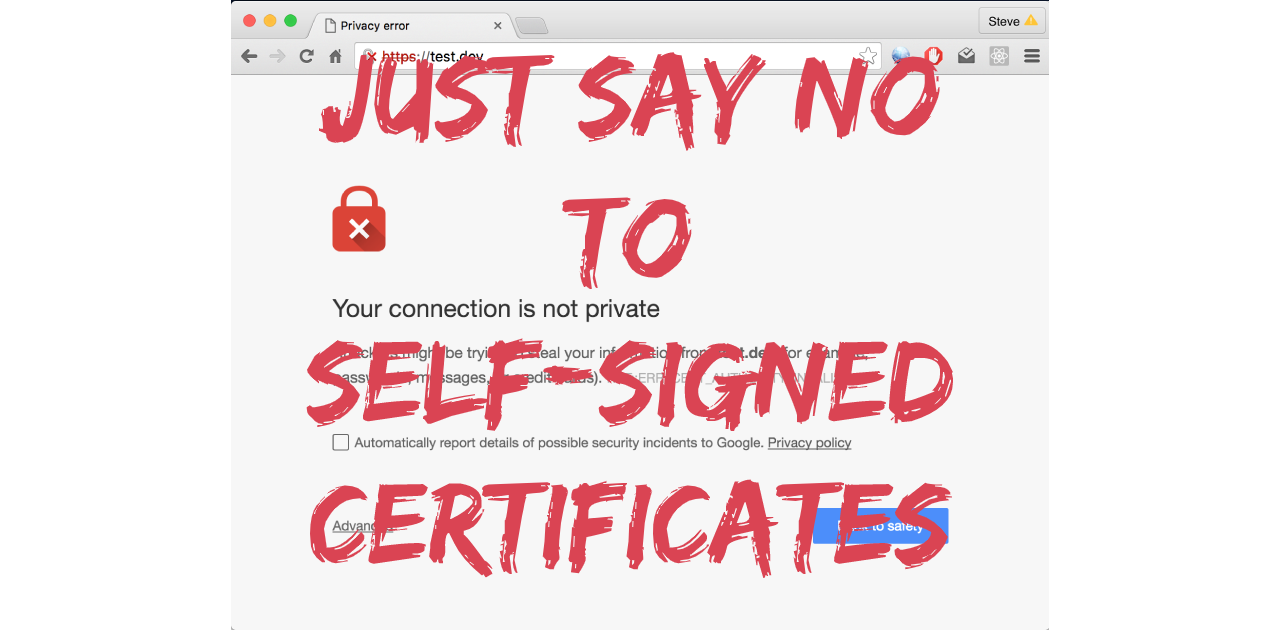
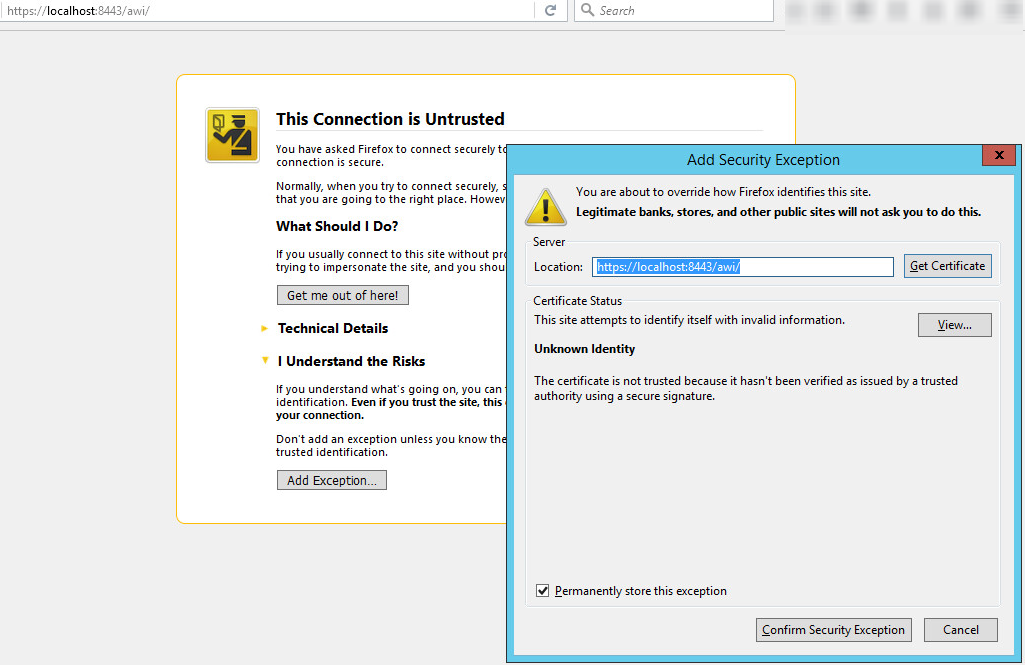
Not trusted by browsers and users
Self-signed certificates contain private and public keys within the same entity, and they cannot be revoked, thus making it difficult to detect security compromises.Pros and cons of self-signed SSL certificates
- Opportunity for unlimited certificate generation.
- No payment required for the signature.
- Quick initiation.
- User personal data set at risk.
- Permanent "unknown publisher" warning.
- Data security is not guaranteed.
Since they are not issued by a recognized CA, web browsers and other client applications will display warning messages, urging caution to users. Risk of compromise. Compromised self-signed certificates can pose many security challenges, since attackers can spoof the identity of the victim.
What are the implications if any to using a self-signed SSL certificate in production : Self-signed TLS/SSL certificates serve a valuable purpose in testing environments by allowing secure communication while awaiting certificates from a public Certificate Authority (CA). However, in live production, their usage can pose significant challenges, leading to reduced website traffic and trust.
Is self-signed certificate a vulnerability
Vulnerabilities in SSL Certificate is a Self Signed is a Medium risk vulnerability that is one of the most frequently found on networks around the world. This issue has been around since at least 1990 but has proven either difficult to detect, difficult to resolve or prone to being overlooked entirely.
Why are self-signed certificates not trusted : Self-signed certificates aren't trusted by browsers because they are generated by your server, not by a CA. You can tell if a certificate is self-signed if a CA is not listed in the issuer field in our SSL Certificate tester.
By default, self-signed certificates will never be trusted by web browsers and operating systems. It is up to each user to bypass the security warning by manually approving each self-sign certificate they encounter, on each device they use, on a case-by-case basis.
By default, self-signed certificates will never be trusted by web browsers and operating systems. It is up to each user to bypass the security warning by manually approving each self-sign certificate they encounter, on each device they use, on a case-by-case basis.
Will self-signed certificates cause browser warnings
Users receive warning messages in their browser when they try to access a web site secured by a self-signed certificate. This is because a trusted Certificate Authority has not signed the certificate.No Trusted Validation – With no external CA validation process, users cannot differentiate between valid and forged self-signed certificates. This enables man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, where attackers insert themselves between connections. They can then decrypt traffic and steal data.Websites need SSL certificates to keep user data secure, verify ownership of the website, prevent attackers from creating a fake version of the site, and convey trust to users.
Using an expired certificate makes clients vulnerable to cyber attacks, which can break their trust. Therefore, it is not recommended to use an expired certificate. A website would not last long with an expired one.
Are self-signed certificates still encrypted : For all they know, a malicious third-party could be redirecting the connection using another self-signed certificate bearing the same holder name. The connection is still encrypted, but does not necessarily lead to its intended target.
How do I know if a certificate is secure : To check an SSL certificate on any website, all you need to do is follow two simple steps.
- First, check if the URL of the website begins with HTTPS, where S indicates it has an SSL certificate.
- Second, click on the padlock icon on the address bar to check all the detailed information related to the certificate.
How a website is trustworthy if it is using SSL certificate
SSL works by ensuring that any data transferred between users and websites, or between two systems, remains impossible to read. It uses encryption algorithms to scramble data in transit, which prevents hackers from reading it as it is sent over the connection.
Without SSL, your site visitors and customers are at higher risk of being having their data stolen. Your site security is also at risk without encryption. SSL protects website from phishing scams, data breaches, and many other threats. Ultimately, It builds a secure environment for both visitors and site owners.Once the certificate expires it is no longer valid. Therefore, once a certificate expires you can safely remove it from the CA database. The one exception to this is if have Key Archival configured on the CA.
Will self-signed signed certificates cause browser warnings : Users receive warning messages in their browser when they try to access a web site secured by a self-signed certificate. This is because a trusted Certificate Authority has not signed the certificate.