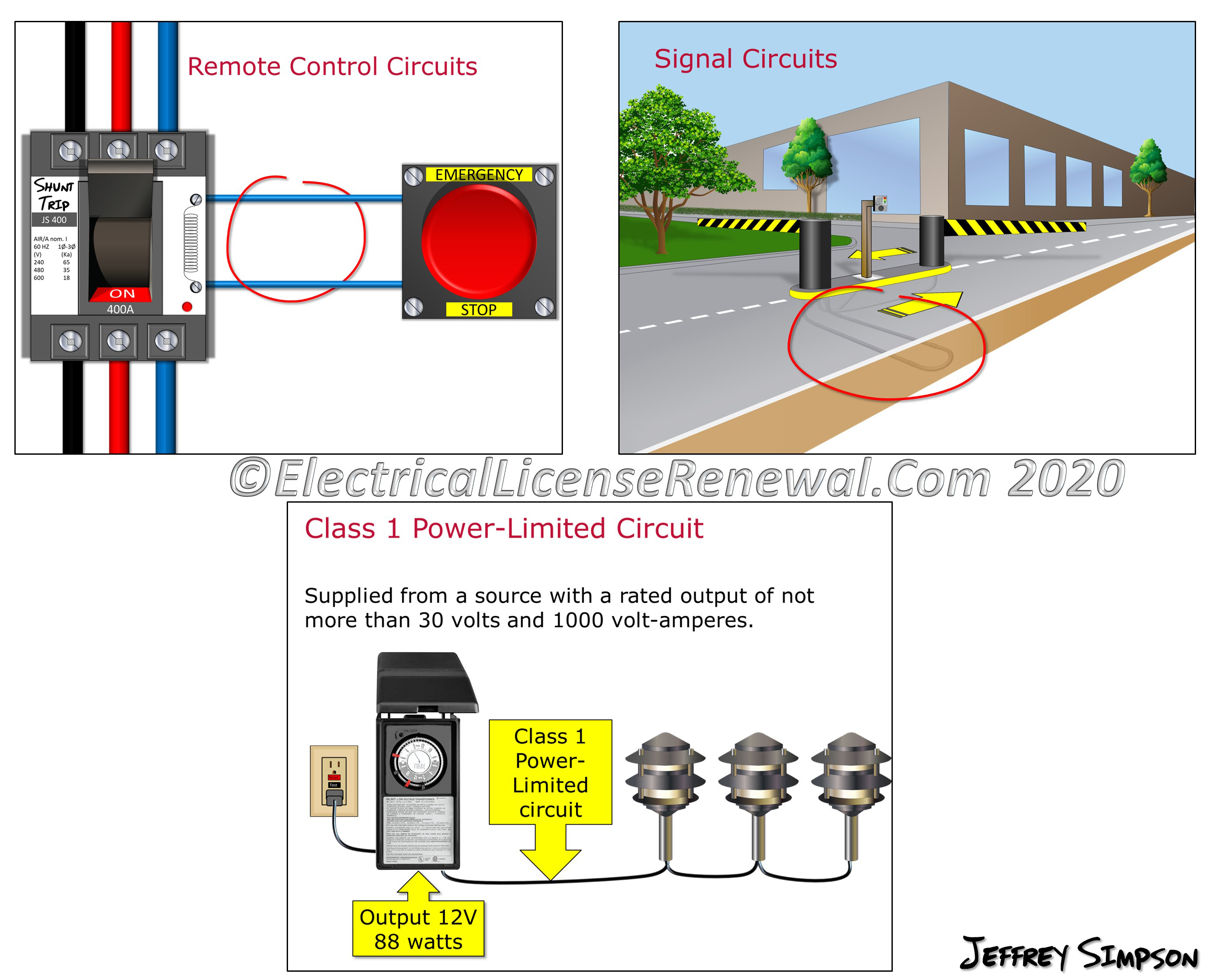
In the simplest terms, a Class 2 circuit is of such low voltage and current, and therefore low power, that it does not present a fire hazard or a shock hazard to personnel. Designs that ensure available energy is limited have many engineering, regulatory, installation, and operational benefits.The amount of 24 volts that our customers need is much greater than the 2 or 3 or 4 amps. So we typically find those 480 volt input power supplies to be 20 or 40 amps. Well.Class 3 circuits are often used for nurse call systems, public address systems, voice intercom systems, and security systems. If the power demand for circuits over 30V is over 0.5VA, but less than 100VA, you'll need a Class 3 circuit.
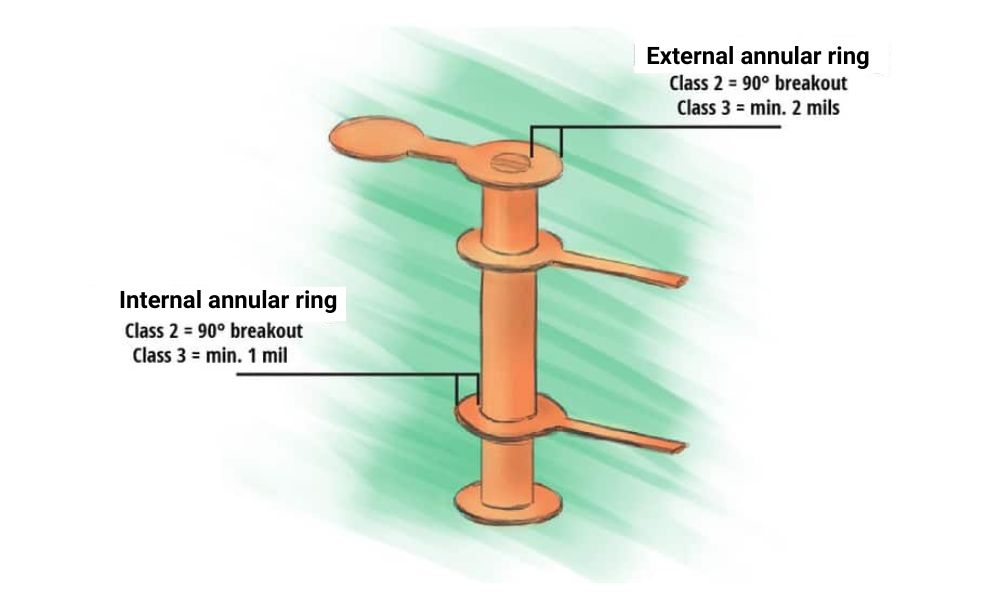
What is a Class 2 or 3 circuit : Class 2 power circuits are limited and do not pose fire initiation risk while providing an acceptable level of protection from electrical shock. Class 3 circuits are limited in output power however, they can and do operate at higher voltage levels and, therefore, can present a shock hazard.
What is class 2 or class 3 circuits
Class 2 power circuits are limited and do not pose fire initiation risk while providing an acceptable level of protection from electrical shock. Class 3 circuits are limited in output power however, they can and do operate at higher voltage levels and, therefore, can present a shock hazard.
How must Class 1 2 and 3 circuits be identified : Class 1, 2 and 3 circuits are defined primarily in terms of the power supply to which they are connected. Power supplies are generally batteries, transformers or electronic power supplies. When working on an existing installation, it is a simple matter of identifying the power source and checking its marking.
Class 3 galvanized wire contains at least 0.80 ounces of zinc per square foot, whereas Class 1 galvanized wire consists of at least 0.28 ounces of zinc per square foot. That is 96% more zinc in the coating to protect your fence wire when you choose Class 3 wire.
Class 2 boards have higher reliability and extended life but allow some cosmetic imperfections. Class 3 PCBs require the highest levels of inspection and testing to ensure uninterrupted service in harsh environments.
What is the difference between Class 1 and Class 3
A Class 1 licence let's you drive your standard big rig, a truck with a large trailer attached to it, air brakes and all. You can also drive almost any other type of vehicle including buses. A Class 3 is more for single vehicles with 3 axles, like a dump truck or large fixed box truck.A Class 1 C+E lorry is an articulated vehicle that bends in the middle and can weigh up to 44 tonne. A Class 2 lorry is any rigid vehicle over 7.5 and up to 32 tonne. You must have completed your LGV Class 2 licence before you are allowed to drive a Class 1 vehicle.Class 2 power circuits are limited and do not pose fire initiation risk while providing an acceptable level of protection from electrical shock. Class 3 circuits are limited in output power however, they can and do operate at higher voltage levels and, therefore, can present a shock hazard.
There are four main types (or 'classes') of National Insurance: Class 1 is payable by employees and employers, Class 2 is a flat rate payable by the self-employed, Class 3 is voluntary contributions paid by people who want to complete their National Insurance record for benefit purposes, but are not otherwise liable to …
What is Class 1 and Class 2 electrical equipment : So essentially Class I equipment has an earth which will be visibly terminated in the plug top & has an earth incorporated in the supply cable. Class II equipment does not rely on an earth connection for safety therefor inside the plug you will only see 2 wires (L+N) & is supplied by a 2 core cable.
What is class 1 or class 2 : Class 1 devices have ground connection so that in case of failure the current escapes to he ground tripping the circuit breaker. Class 2 are double insulated. This means there are two levels of insulation. Often the case is plastic which acts as one level. A single failure should not cause shock on them.
What is a Class 3 electrical item
Class 'III'
Appliances that operate at SELV (Separated Extra Low Voltage) are deemed to be class 3. This basically means the device cannot produce enough voltage to risk the user getting an electric shock. Generally, the power output of these items is 50vac or 120vdc.
Appliances that operate at SELV (Separated Extra Low Voltage) are deemed to be class 3. This basically means the device cannot produce enough voltage to risk the user getting an electric shock. Generally, the power output of these items is 50vac or 120vdc.So essentially Class I equipment has an earth which will be visibly terminated in the plug top & has an earth incorporated in the supply cable. Class II equipment does not rely on an earth connection for safety therefor inside the plug you will only see 2 wires (L+N) & is supplied by a 2 core cable.
What is a Class 3 electrical circuit : Class 3 circuits are often used for nurse call systems, public address systems, voice intercom systems, and security systems. If the power demand for circuits over 30V is over 0.5VA, but less than 100VA, you'll need a Class 3 circuit.



